Ellen Thomas, University Professor in the College of Integrative Sciences and research professor of earth and environmental sciences, is a co-author of a paper titled "Very Large Release of Mostly Volcanic Carbon During the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum," published in the weekly science journal Nature on Aug. 31. The study focused on Palaeocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum, a surface warming event associated with ecological disruption that occurred about 56 million years ago, releasing a large amount of carbon. The researchers combined boron and carbon isotope data in an Earth system model and found that the source of carbon was much larger than previously thought. Most…
The availability of sufficient dissolved oxygen in seawater is critical for marine life, and places where oxygen falls below a critical concentration — or "dead zones" — are often associated with mass die-offs of fish, shrimp and other creatures. With future global warming, the oceans are on course to see progressively less dissolved oxygen available. Scientists currently use often not well-tested computer models to predict the expansion of dead zones, but a team of researchers from Wesleyan, University California Riverside and Syracuse University are hoping to use oceanic sediment samples to better predict where die-offs may occur next. Their study,…
For her outstanding efforts in pioneering studies in micropalaeontology and natural history, The Micropalaeontological Society (TMS) awarded Wesleyan's Ellen Thomas with the 2016 Brady Medal. The Brady Medal is TMS's most prestigious honor and is awarded to scientists who have had a major influence on micropalaeontology by means of a substantial body of research. Thomas was honored for "communicating to an extremely broad audience fascinating, impactful and often thought-provoking research" and "academic encouragement of students and peers over the years with [her] generosity of time in a very busy and successful career," noted TMS President F. John Gregory. Thomas, research professor…
Ellen Thomas, research professor of earth and environmental sciences, is the co-author of "Pteropoda (Mollusca, Gastropoda, Thecosomata) from the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum of the United States Atlantic Coastal Plain," published in Palaeontologia Electronica, Article 19 (3) in October 2016. The Paleocene Epoch lasted 65 to 54.8 million years ago and the Eocene Epoch lasted from 56 to 33.9 million years ago, and was a period of rapid global warming. The response of many organisms to the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM) has been documented, but marine mollusks are not known from any deposits of that age. For the first time, Thomas and her…
Ellen Thomas, professor of earth and environmental sciences and University Professor in the College of Integrative Sciences, recently co-authored five papers in academic journals. Her first paper, “Jianshuiite in Oceanic Manganese Nodules” co-authored with Jeffery Post and Peter Heaney, appeared within American Mineralogist. Deviating from her usual research, Thomas focused on mineralogy and, in particular, the crystal structure of a rare mineral found in sediments during an ancient counterpart of future global warming. Thomas co-authored “Variability in Climate and Productivity during the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum in the Western Tethys,” with Flavia Boscolo-Galazzo and Luca Giusberti, both of the University of Padova.…
Ellen Thomas, the University Professor in the College of Integrative Sciences, research professor of earth and environmental science, is the co-author of two recently published papers. They include: "Microfossil evidence for trophic changes during the Eocene–Oligocene transition in the South Atlantic (ODP Site 1263, Walvis Ridge)," published in Climate of the Past, Volume 11, pages 1249–1270 in September 2015 and "Changes in benthic ecosystems and ocean circulation in the Southeast Atlantic across Eocene Thermal Maximum 2," published in the journal Paleoceanography, Volume 30, pages 1059-1077 in August 2015. "Microfossil evidence" describes changes in organisms living in the oceans during a major change in the…
Ellen Thomas, the University Professor in the College of Integrative Sciences, received a grant in August from the National Science Foundation to support her research on “Evaluating Deep-Sea Ventilation and the Global Carbon Cycle during early Paleocene Hyperthemals.” The $105,000 award is part of a combined $619,000 grant shared with Yale University and the University of Texas at Arlington. Rapid, short-term global warming events in the Early Paleogene (~65-45 million years ago) were caused by massive greenhouse gas release into the ocean-atmosphere system. These warming events, called hyperthermals, had far-reaching effects on the evolution of life on Earth, ecosystems and…
Ellen Thomas, research professor of earth and environmental sciences, is the co-author of four recenty-published papers. They include: "Deep-sea benthic foraminiferal turnover during the early middle Eocene transition at Walvis Ridge (SE Atlantic)," published in Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, Issue 417: pages 126-136, January 2015. The paper's co-author, Silvia Ortiz, was a PhD student at the University of Zaragoza, and spent several months at Wesleyan working with Thomas. (more…)
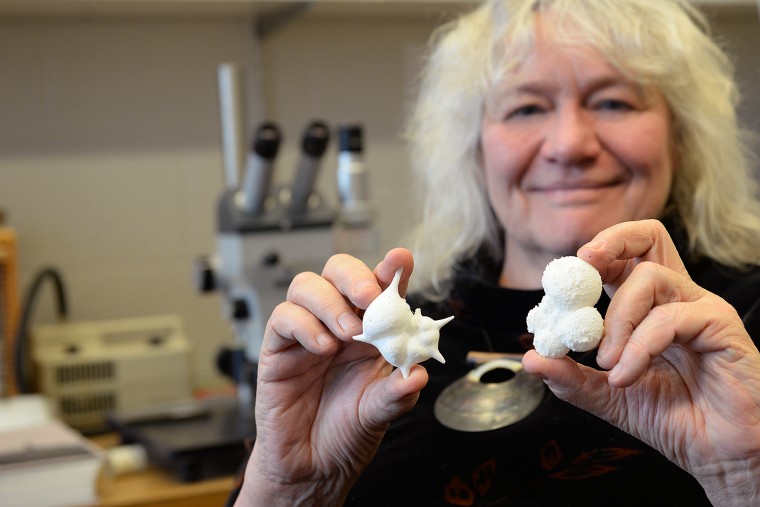
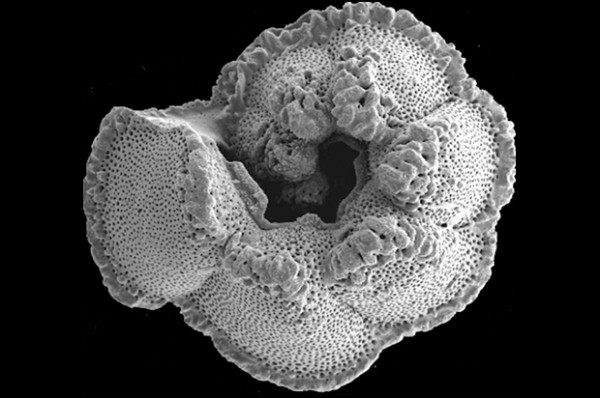
#THISISWHY Research Professor Ellen Thomas grasps a glass-enclosed sample of hundreds of microfossils, each a white fleck of limestone barely visible to the human eye. "The first time students look at these they say, 'they all look the same to me,' but in reality, they are all have very different shapes," Thomas says. "Even under a microscope, it can be difficult for a new eye to see the differences, but each species has its own shape; some have a much more open, light structure because they lived floating in the oceans close to the surface. Others have denser shells and lived on the bottom of the ocean,…
Wesleyan faculty Joop Varekamp and Ellen Thomas are among the authors of a paper on rates of sea-level rise along the eastern U.S. seaboard titled "Late Holocene sea level variability and Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation," published in the journal Paleoceanography, Volume 29, Issue 8, pages 765–777 in August 2014. Varekamp is the Harold T. Stearns Professor of Earth Science, professor of earth and environmental sciences and professor of environmental studies. Thomas is research professor of earth and environmental sciences at Wesleyan, and also a senior research scientist in geology and geophysics at Yale University. Pre-20th century sea level variability remains poorly understood due to…
Ellen Thomas, research professor of earth and environmental sciences, is the author of a paper titled "Rapid and sustained surface ocean acidification during the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum," published in Paleoceanography, May 2014. In this paper Thomas and her colleagues document that ocean acidification of the surface ocean not only occurred during past times of global warming and high CO2 levels, but also by how much — about 0.3 pH units. The group studied planktic foraminifers from a drill site in the North Pacific. Thomas' study has been highlighted in a press release from Columbia University and also on Phys.org.
Ellen Thomas, research professor of earth and environmental sciences, is the co-author of a paper titled "Carbon Sequestration during the Palaeocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum by an Efficient Biological Pump," published in the April 2014 edition of Nature Geoscience. In the paper, Thomas explains how ocean-dwelling bacteria may have vacuumed up carbon and halted a period of extreme warmth some 56 million years ago. The finding suggests how Earth might once have rapidly reversed a runaway greenhouse effect. Its effect on global oceanic productivity is controversial. In the paper, Thomas and her colleagues present records of marine barite accumulation rates that show distinct peaks during…